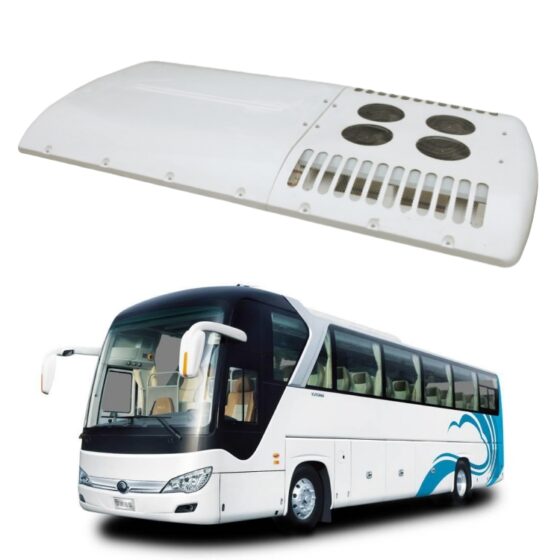
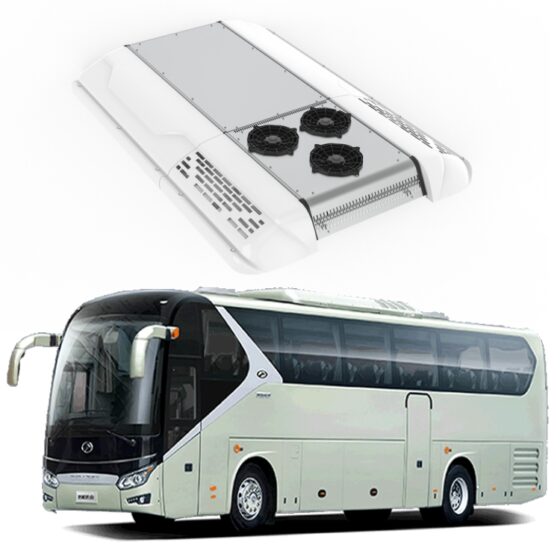
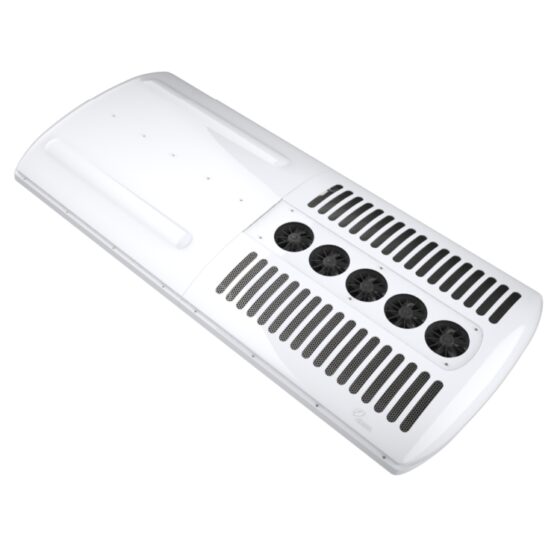
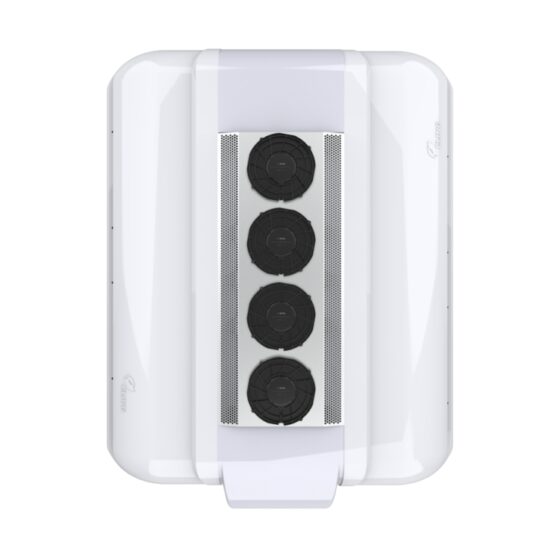
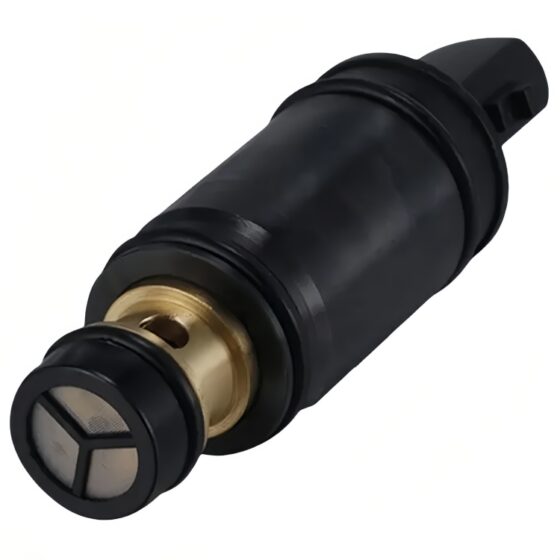
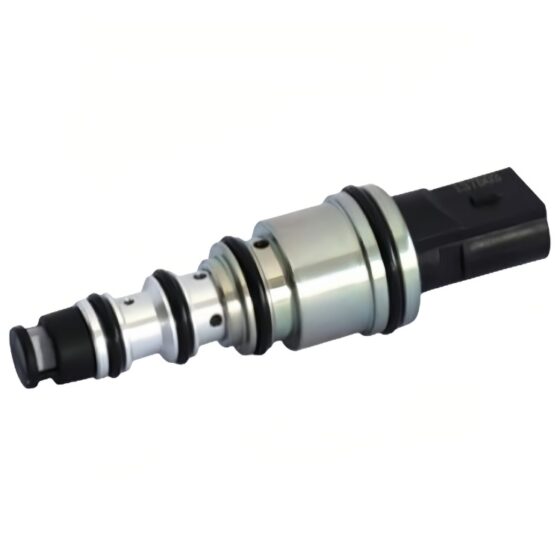
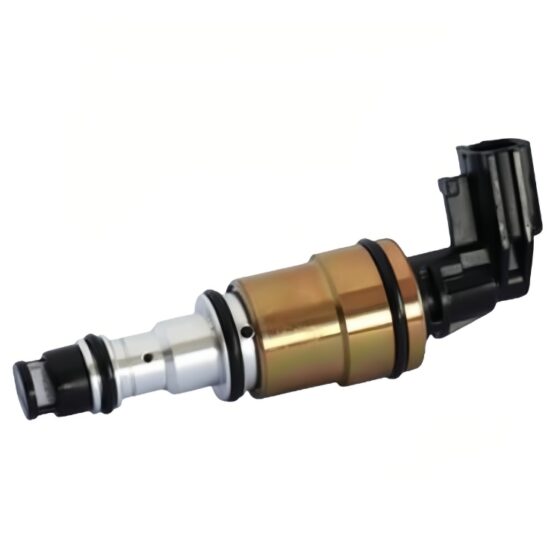
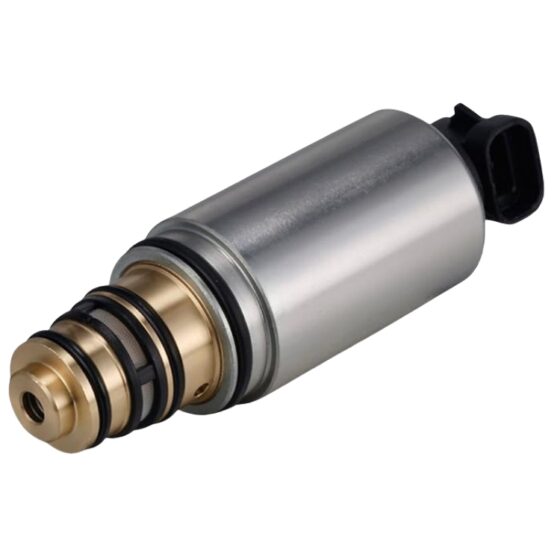
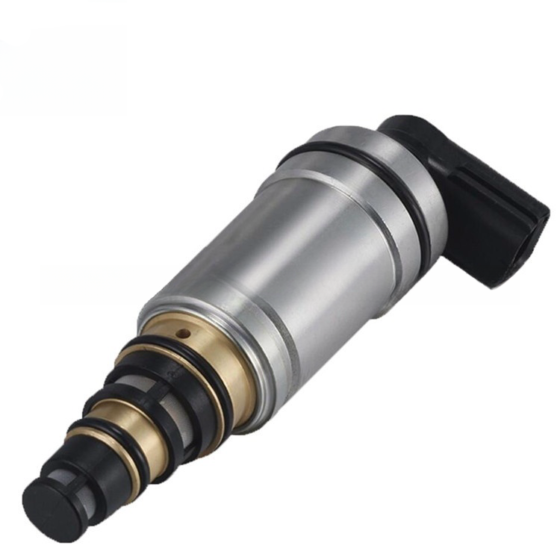
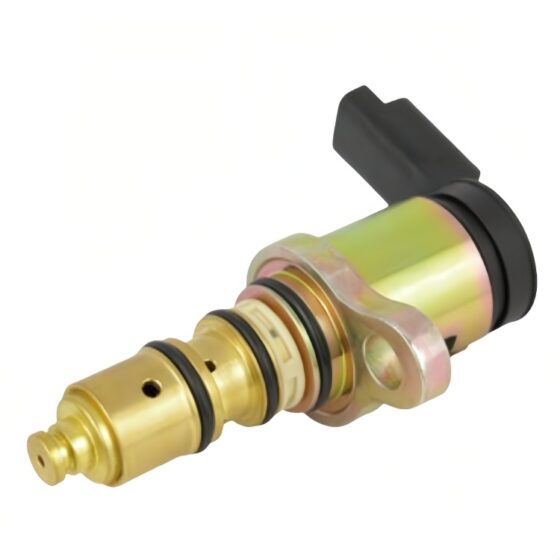
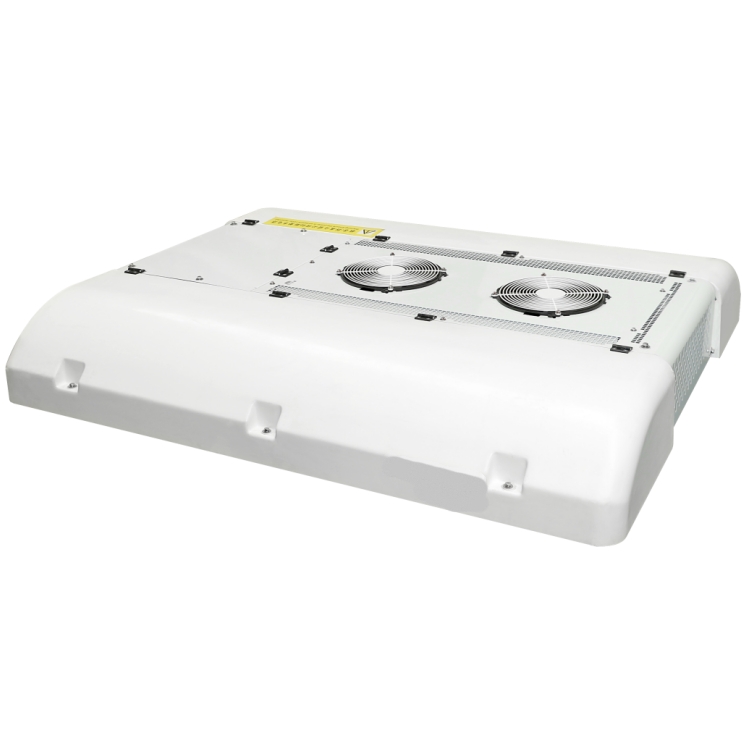
Die Standklimaanlage ist eine Art Raumklimaanlage. Das Gerät bezieht sich auf die Verwendung einer am Fahrzeug montierten Batterie-Gleichstromversorgung (12V/24V/36V) um die Klimaanlage während des Parkens kontinuierlich zu betreiben, Warten, und Ruhe, und um die Temperatur einzustellen und zu steuern, Feuchtigkeit, Durchflussmenge, und andere Parameter der Umgebungsluft im Fahrzeuginnenraum, Vollständige Erfüllung der komfortablen Kühlbedürfnisse von Lkw-Fahrern. Aufgrund der begrenzten Batteriekapazität der Autobatterie und der schlechten Benutzererfahrung mit der Heizung im Winter, Die Standklimaanlage wird hauptsächlich einzeln gekühlt. Es umfasst im Allgemeinen Systeme zur Förderung von Kältemittelmedien, Kaltquellen-Ausrüstung, Endgeräte, und andere Hilfssysteme. Hauptsächlich einschließlich: Kondensator, Verdampfer, Elektrisches Steuerungssystem, Kompressor, Ventilator, und Rohrleitungssystem. Das Endgerät nutzt die Kälteenergie aus der Übertragung und Verteilung, um die Klimatisierung in der Kabine gezielt zu steuern, Bereitstellung einer komfortablen Ruheumgebung für Lkw-Fahrer.

Bus HVAC System
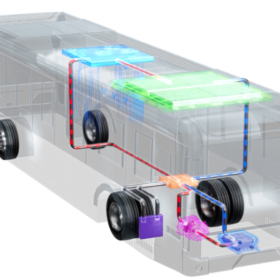
A heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system in a vehicle is used to control the internal temperature of the vehicle cabin. It includes three subsystems, namely, heating, cooling, and air conditioning, that work together to provide purified air to the vehicle cabin, ensuring thermal comfort to drivers and passengers. It controls the air temperature, inspects the moisture content in the air, and eliminates excessive humidity from the circulating air.The bus HVAC unit consists of the primary component unit that includes compressor, Kondensator, Verdampfer, pressure regulating devices, orifice tube, thermal expansion valve, receiver-drier, and accumulator. The compressor is considered the core component of the overall automobile HVAC system. The compressor helps in compressing and transferring refrigerant gas. A condenser is used to help radiate heat, when the hot compressed gases are introduced on the top of a condenser, they are cooled instantly and after the cooling is complete, they condense and exit from the bottom of the condenser as a high-pressure fluid. An evaporator is a heat absorber component of the HVAC system. The main purpose of an evaporator is to remove the heat from inside the vehicle and dehumidify the environment within it. Pressure regulating devices are meant for controlling the evaporator temperature by regulating the refrigerant pressure and flow into the evaporator.The bus HVAC market is segmented into type, vehicle type, sales channel, input, vehicle type by propulsion and region. By type, it is further divided into automatic, and manual. By vehicle type, the Bus HVAC industry is segmented into intercity buses that are subdivided into 9m, 10m, and 12m; coach buses that are further segmented into 9m, 10m, and 12m; school buses that are further segmented into 9m, 10m, and 12m, and transit buses that are further segmented into 9m, 10m, and 12m. By sales channel, the market is segmented into original equipment manufacturers, and aftermarket etc.
Technische Parameter
Micro-channel heat exchanger, 26% reduction in weight, 5% reduction in fuel consumption, heat exchange efficiency improved 20%, refrigerant charged 50% less, cooling capacity 10% larger.
100% DACROMET Anti-corrosion Coated Coil
800 hours salt spary test, suitable for harsh enviroment.
Patented CAN Control
Modular design, digital communication;PWM control module, evaporator fan stepless speed regulation; smart condenser fan control, cooling on demand.
Thermal Insulation Materials
Environmentally friendly, antiseptic, odourless and flame-retardant.
The working principle of bus air conditioning is similar to most household air conditioners, which transfer heat between indoor and outdoor through refrigerant circulation to achieve cooling effect. The air conditioning system consists of four main components: Kompressor, Kondensator, expansion valve, and evaporator. The refrigerant is compressed into high-temperature and high-pressure gas in the compressor, and then cooled by the condenser to release heat, becoming a high-pressure liquid. Nächster, it enters the expansion valve and is cooled down by reducing pressure, becoming a low-pressure liquid. Finally, the refrigerant in the evaporator absorbs the heat inside the car and becomes a low-temperature and low-pressure gas, which flows back to the compressor for circulation. Bus air conditioning is mainly divided into three types: roof mounted air conditioning, trunk type air conditioning, and split type air conditioning. Among them, roof mounted air conditioning is the most common type, which involves hanging the air conditioning unit on the roof for cooling. The box type air conditioner is directly placed on the partition inside or outside the carriage, making it easy to install and maintain. Split type air conditioning separates the cold and heat sources, and uses matching evaporators and air conditioning units to achieve cooling and ventilation.
 Suzhou Roger Autoteile Co., GmbH.
Suzhou Roger Autoteile Co., GmbH.










 Unser Unternehmen verfügt über langjährige Branchenerfahrung, mit Innovation und exzellenter Servicequalität als zentrale Wettbewerbsfähigkeit, Wir sind bestrebt, unseren Kunden Produkte und Dienstleistungen von höchster Qualität zu bieten. Als führendes Unternehmen in der Branche, Wir halten uns stets an die Orientierung an den Kundenbedürfnissen, und durch kontinuierliche technologische Forschung und Entwicklung sowie Prozessverbesserung, Unsere Produkte haben herausragende Wettbewerbsvorteile auf dem Markt.
Unser Unternehmen verfügt über langjährige Branchenerfahrung, mit Innovation und exzellenter Servicequalität als zentrale Wettbewerbsfähigkeit, Wir sind bestrebt, unseren Kunden Produkte und Dienstleistungen von höchster Qualität zu bieten. Als führendes Unternehmen in der Branche, Wir halten uns stets an die Orientierung an den Kundenbedürfnissen, und durch kontinuierliche technologische Forschung und Entwicklung sowie Prozessverbesserung, Unsere Produkte haben herausragende Wettbewerbsvorteile auf dem Markt.









